环境问题:
首先是在vs中安装opencv和eigen两个库
安装eigen库所推荐的链接:
VS2019正确的安装Eigen库,解决所有报错(全网最详细!!)_MaybeTnT的博客-CSDN博客_vs2019安装eigen
https://blog.csdn.net/MaybeTnT/article/details/109841378安装opencv和eigen库是类似的,就连配置过程都很相似。都是需要先去下载相关的库,然后在vs中进行配置就行了。
项目-》右键-》属性-》vc++目录-》包含目录-》添加相应的依赖库就可以。
其中在包含目录中添加:
E:\OpenCV\opencv\build\include
E:\OpenCV\opencv\build\include\opencv2
D:\eigen3
注意:这是你下载的opencv和eigen所在的路径
在库目录中添加:
E:\OpenCV\opencv\build\x64\vc14\lib

两个库安装完成后就可以运行代码了,这里我使用的是《视觉slam14讲》,第8节的光流法的实现。
代码如下:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <chrono>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/types_c.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
string file_1 = "C:\\Users\\ThinkPad\\Desktop\\LK1.png"; // first image
string file_2 = "C:\\Users\\ThinkPad\\Desktop\\LK2.png"; // second image
/// Optical flow tracker and interface
class OpticalFlowTracker {
public:
OpticalFlowTracker(
const Mat& img1_,
const Mat& img2_,
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1_,
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2_,
vector<bool>& success_,
bool inverse_ = true, bool has_initial_ = false) :
img1(img1_), img2(img2_), kp1(kp1_), kp2(kp2_), success(success_), inverse(inverse_),
has_initial(has_initial_) {}
void calculateOpticalFlow(const Range& range);
private:
const Mat& img1;
const Mat& img2;
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1;
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2;
vector<bool>& success;
bool inverse = true;
bool has_initial = false;
};
/**
* single level optical flow
* @param [in] img1 the first image
* @param [in] img2 the second image
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [in|out] kp2 keypoints in img2, if empty, use initial guess in kp1
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse use inverse formulation?
*/
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat& img1,
const Mat& img2,
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1,
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2,
vector<bool>& success,
bool inverse = false,
bool has_initial_guess = false
);
/**
* multi level optical flow, scale of pyramid is set to 2 by default
* the image pyramid will be create inside the function
* @param [in] img1 the first pyramid
* @param [in] img2 the second pyramid
* @param [in] kp1 keypoints in img1
* @param [out] kp2 keypoints in img2
* @param [out] success true if a keypoint is tracked successfully
* @param [in] inverse set true to enable inverse formulation
*/
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat& img1,
const Mat& img2,
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1,
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2,
vector<bool>& success,
bool inverse = false
);
/**
* get a gray scale value from reference image (bi-linear interpolated)
* @param img
* @param x
* @param y
* @return the interpolated value of this pixel
*/
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat& img, float x, float y) {
// boundary check
if (x < 0) x = 0;
if (y < 0) y = 0;
if (x >= img.cols) x = img.cols - 1;
if (y >= img.rows) y = img.rows - 1;
uchar* data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
// images, note they are CV_8UC1, not CV_8UC3
Mat img1 = imread(file_1, 0);
Mat img2 = imread(file_2, 0);
// key points, using GFTT here.
vector<KeyPoint> kp1;
Ptr<GFTTDetector> detector = GFTTDetector::create(500, 0.01, 20); // maximum 500 keypoints
detector->detect(img1, kp1);
// now lets track these key points in the second image
// first use single level LK in the validation picture
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_single;
vector<bool> success_single;
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_single, success_single);
// then test multi-level LK
vector<KeyPoint> kp2_multi;
vector<bool> success_multi;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowMultiLevel(img1, img2, kp1, kp2_multi, success_multi, true);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by gauss-newton: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// use opencv's flow for validation
vector<Point2f> pt1, pt2;
for (auto& kp : kp1) pt1.push_back(kp.pt);
vector<uchar> status;
vector<float> error;
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
cv::calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(img1, img2, pt1, pt2, status, error);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "optical flow by opencv: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// plot the differences of those functions
Mat img2_single;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_single, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_single.size(); i++) {
if (success_single[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_single, kp2_single[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_single, kp1[i].pt, kp2_single[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_multi;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_multi, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < kp2_multi.size(); i++) {
if (success_multi[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_multi, kp2_multi[i].pt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_multi, kp1[i].pt, kp2_multi[i].pt, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
Mat img2_CV;
cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_CV, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (int i = 0; i < pt2.size(); i++) {
if (status[i]) {
cv::circle(img2_CV, pt2[i], 2, cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0), 2);
cv::line(img2_CV, pt1[i], pt2[i], cv::Scalar(0, 250, 0));
}
}
cv::imshow("tracked single level", img2_single);
cv::imshow("tracked multi level", img2_multi);
cv::imshow("tracked by opencv", img2_CV);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void OpticalFlowSingleLevel(
const Mat& img1,
const Mat& img2,
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1,
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2,
vector<bool>& success,
bool inverse, bool has_initial) {
kp2.resize(kp1.size());
success.resize(kp1.size());
OpticalFlowTracker tracker(img1, img2, kp1, kp2, success, inverse, has_initial);
parallel_for_(Range(0, kp1.size()),
std::bind(&OpticalFlowTracker::calculateOpticalFlow, &tracker, placeholders::_1));
}
void OpticalFlowTracker::calculateOpticalFlow(const Range& range) {
// parameters
int half_patch_size = 4;
int iterations = 10;
for (size_t i = range.start; i < range.end; i++) {
auto kp = kp1[i];
double dx = 0, dy = 0; // dx,dy need to be estimated
if (has_initial) {
dx = kp2[i].pt.x - kp.pt.x;
dy = kp2[i].pt.y - kp.pt.y;
}
double cost = 0, lastCost = 0;
bool succ = true; // indicate if this point succeeded
// Gauss-Newton iterations
Eigen::Matrix2d H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero(); // hessian
Eigen::Vector2d b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero(); // bias
Eigen::Vector2d J; // jacobian
for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) {
if (inverse == false) {
H = Eigen::Matrix2d::Zero();
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
}
else {
// only reset b
b = Eigen::Vector2d::Zero();
}
cost = 0;
// compute cost and jacobian
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x < half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y < half_patch_size; y++) {
double error = GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + x + dx, kp.pt.y + y + dy);; // Jacobian
if (inverse == false) {
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x + 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x - 1, kp.pt.y + dy + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img2, kp.pt.x + dx + x, kp.pt.y + dy + y - 1))
);
}
else if (iter == 0) {
// in inverse mode, J keeps same for all iterations
// NOTE this J does not change when dx, dy is updated, so we can store it and only compute error
J = -1.0 * Eigen::Vector2d(
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x + 1, kp.pt.y + y) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x - 1, kp.pt.y + y)),
0.5 * (GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y + 1) -
GetPixelValue(img1, kp.pt.x + x, kp.pt.y + y - 1))
);
}
// compute H, b and set cost;
b += -error * J;
cost += error * error;
if (inverse == false || iter == 0) {
// also update H
H += J * J.transpose();
}
}
// compute update
Eigen::Vector2d update = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (std::isnan(update[0])) {
// sometimes occurred when we have a black or white patch and H is irreversible
cout << "update is nan" << endl;
succ = false;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost > lastCost) {
break;
}
// update dx, dy
dx += update[0];
dy += update[1];
lastCost = cost;
succ = true;
if (update.norm() < 1e-2) {
// converge
break;
}
}
success[i] = succ;
// set kp2
kp2[i].pt = kp.pt + Point2f(dx, dy);
}
}
void OpticalFlowMultiLevel(
const Mat& img1,
const Mat& img2,
const vector<KeyPoint>& kp1,
vector<KeyPoint>& kp2,
vector<bool>& success,
bool inverse) {
// parameters
int pyramids = 4;
double pyramid_scale = 0.5;
double scales[] = { 1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125 };
// create pyramids
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
vector<Mat> pyr1, pyr2; // image pyramids
for (int i = 0; i < pyramids; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
pyr1.push_back(img1);
pyr2.push_back(img2);
}
else {
Mat img1_pyr, img2_pyr;
cv::resize(pyr1[i - 1], img1_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr1[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr1[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
cv::resize(pyr2[i - 1], img2_pyr,
cv::Size(pyr2[i - 1].cols * pyramid_scale, pyr2[i - 1].rows * pyramid_scale));
pyr1.push_back(img1_pyr);
pyr2.push_back(img2_pyr);
}
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "build pyramid time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
// coarse-to-fine LK tracking in pyramids
vector<KeyPoint> kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr;
for (auto& kp : kp1) {
auto kp_top = kp;
kp_top.pt *= scales[pyramids - 1];
kp1_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
kp2_pyr.push_back(kp_top);
}
for (int level = pyramids - 1; level >= 0; level--) {
// from coarse to fine
success.clear();
t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
OpticalFlowSingleLevel(pyr1[level], pyr2[level], kp1_pyr, kp2_pyr, success, inverse, true);
t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "track pyr " << level << " cost time: " << time_used.count() << endl;
if (level > 0) {
for (auto& kp : kp1_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
for (auto& kp : kp2_pyr)
kp.pt /= pyramid_scale;
}
}
for (auto& kp : kp2_pyr)
kp2.push_back(kp);
}
其中在运行过程中出现的问题内存异常
提示:
有未经处理的异常:Microsoft C++异常:cv::Exception,位于内存位置******处
解决方式是图片的路径存在问题:
string file_1 = "C:\\Users\\ThinkPad\\Desktop\\LK1.png"; // first image string file_2 = "C:\\Users\\ThinkPad\\Desktop\\LK2.png"; // second image需要换成绝对路径就可以了。并且绝对路径是两个斜杠并非一个,如图所示:
运行结果如图:
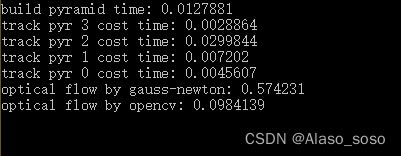
由于并行化程序在每次运行时的表现不尽相同,在你们的运行结果中,这些数字不会精确相同,在我的结果中,反而是opencv的运行速度比高斯牛顿法更快。
单层光流:
多层光流: 
opencv光流法:
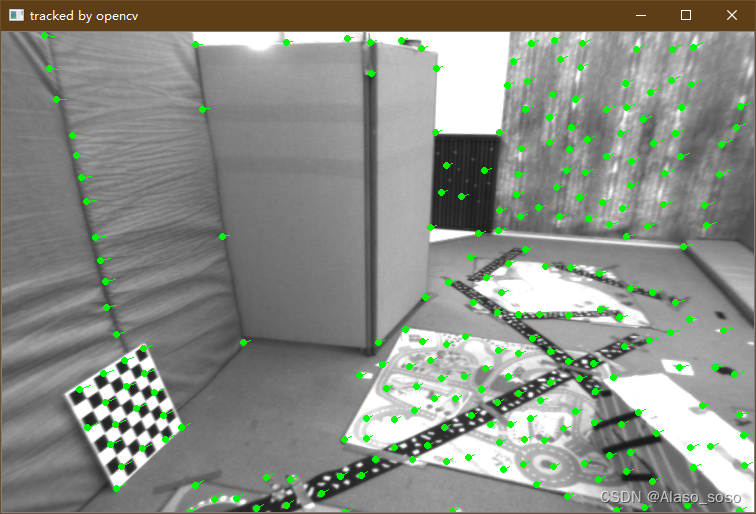
从效果中可以看出,单层光流效果差一点,多层光流与opencv效果相当。考虑时间我的opencv效果更好。
转载自CSDN-专业IT技术社区
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44808827/article/details/124481658




